Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is the latest widely adopted practice in hair restoration. Traditionally, hairs to be transplanted are taken from a strip of hair at the back of the scalp. The hairs are then dissected out of he strip of skin and hair. Follicular unit extraction involves removing each follicular unit to be transplanted individually, leaving only a small hole where the follicle used to be. The advantage of FUE is that involves minimal scarring and no chance of an unwanted large scar where the strip of hair would be removed. The small holes also feel much faster and with less pain and tenderness than the strip method. Sounds great, right? Well there disadvantages. The main disadvantages are that the cost can be twice as much due to it being more time and labor intensive as well as less donor hair available since the surgeon must leave some hair in between the hair follicles which are removed. Below is a more complete list of advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- No linear scar
- Important for those who wear their hair short
- Decreases healing time in the donor area
- Useful for those with a greater risk of donor scarring (Asians)
- Ideal for repairing donor scars that cannot be excised
- No limitations on strenuous exercise after the procedure
- Less post-op discomfort
- Provides an alternative when the scalp is too tight for a strip excision
- Extends the dimensions of the donor area (but not necessarily the total number of grafts)
- Enables one to harvest finer hair from the nape of the neck to be used at the hairline or for eyebrows
- Makes it theoretically possible to harvest non-scalp hair
- ex. beard or body hair
- Most useful when a limited number of grafts are needed
Disadvantages
- Maximum follicular unit graft yield is lower than with FUT
- Due to the inability to harvest all the hair from the mid-permanent zone
- The scarring and distortion of the donor scalp from FUE makes subsequent FUE sessions more difficult
- Greater follicular transection (damage) compared to FUT
- Greater patient variability in who are good candidates compared to FUT
- More difficult to capture the entire follicular unit
- More difficult to obtain a natural distribution of follicular units
- For efficiency, the largest follicular units are targeted, but these may not be ideal for the hairline
- Grafts are more fragile and subject to trauma during placing
- Since they often lack the protective dermis and fat of microscopically dissected grafts
- Microscopic dissection may still be needed
- If the number of single-hair grafts is inadequate
- To remove hair fragments
- Grafts harvested from outside the donor area will not be permanent
- After large numbers of graft are harvested, fine stippled scars may become visible due to thinning of donor area
- Size of session is limited
- Requires multiple sessions to equal the size of a single FUT
- Takes longer to perform
- More expensive than FUT
- Problems of “capping”
- This occurs when the top of the graft pulls off during extraction
- Problems of buried grafts
- This occurs during the blunt phase of the three-step technique when the graft is pushed into the fat and must be removed through a small incision or risked producing a cyst
Photos of Follicular Unit Extraction punch holes
FUE leaves small holes which can heal on their own, without special care by the doctor. Below is an example of healing in a patient who had 600 grafts.
After Hair Transplant
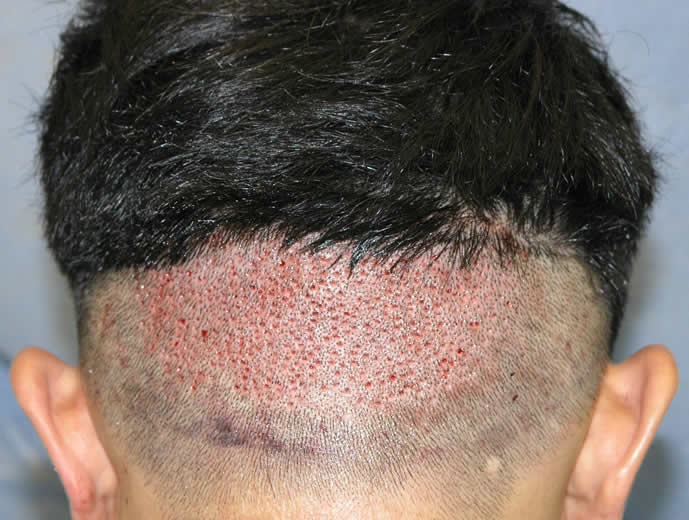
6 Days After Hair Transplant
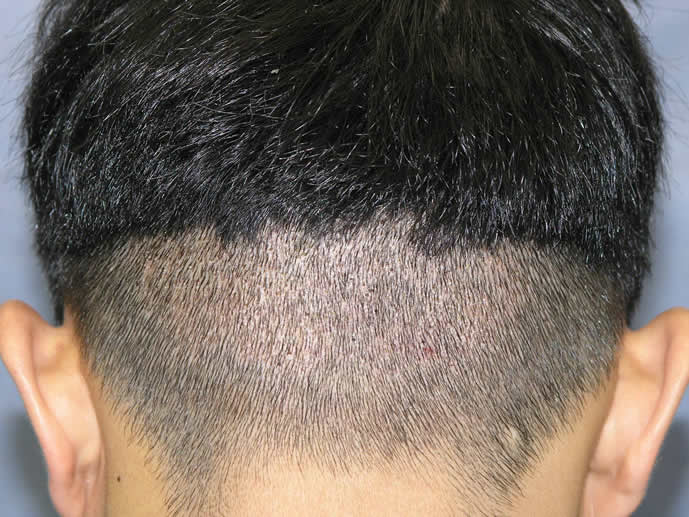
13 Days After Hair Transplant

Follicular Unit Extraction Variations
With the acceptance of follicular unit extraction has come a number of improvements and variations. These variations have caused some confusion among hair transplant consumers who do not know the differences between them or what they mean to the average patient.
3-Step Follicular Unit Extraction
 The 3-step technique is the most commonly used today. The original follicular unit extraction technique used a sharp 1mm round punch tool to cut the tissue surrounding the follicle and then the folicle was removed. Because the follicle cannot be seen below the skin, this led to the sharp device frequently transecting (cutting) the hair follicle, potentially making it useless.
The 3-step technique is the most commonly used today. The original follicular unit extraction technique used a sharp 1mm round punch tool to cut the tissue surrounding the follicle and then the folicle was removed. Because the follicle cannot be seen below the skin, this led to the sharp device frequently transecting (cutting) the hair follicle, potentially making it useless.
In the 3 step technique, the sharp hole punch is only used to cut the visible surface of the skin. Then a blunt hole punch is used to cut the rest of the way around the follicle – this is known as blunt dissection. Because it is not sharp, damage to the follicular unit is much less common. The third step is removal of the graft.
One of the disadvantages of the 3-step technique is that he blunt punch can end up pushing the follicular unit underneath the skin. Sometimes the follicular unit can still be removed manually or by cutting a small slit, but if not a cyst can for under the skin that will have to be taken care of later.
RotoCore
 An issue with both the 2 and 3-step FUE methods is that it can be difficult to maintain a straight cutting path. This in turn causes poor alignment with the follicle leading to potential damage and transection of the follicle itself. Typical 2 and 3-step FUE punches have to be rotated as they cut into the scalp and during long transplant sections this leads to fatigue on the part of the hair transplant section which can also increase damage to the follicle. Other issues include buildup of waste debris in the punch itself and a lack of depth control that allows the punch to cut too shallow or too deep.
An issue with both the 2 and 3-step FUE methods is that it can be difficult to maintain a straight cutting path. This in turn causes poor alignment with the follicle leading to potential damage and transection of the follicle itself. Typical 2 and 3-step FUE punches have to be rotated as they cut into the scalp and during long transplant sections this leads to fatigue on the part of the hair transplant section which can also increase damage to the follicle. Other issues include buildup of waste debris in the punch itself and a lack of depth control that allows the punch to cut too shallow or too deep.
The RotoCore device solves these issues by automatically rotating as it is inserted into the scalp, alleviating the doctor from manually rotating the punch. It allows for easier debris removal from the device and allows the surgeon to set depth control based on each individual’s needs.
NeoGraft
 The NeoGraft system is a mechanically assisted FUE device which greatly speeds up the removal of follicular unit grafts from the donor area. One of the main drawbacks of follicular unit extraction is that it is a time consuming process which limits the amount of hairs that can be transplanted in one session. With the NeoGraft device, it is possible to perform larger mega-session style transplants in the same time as a normal manual FUE hair transplant.
The NeoGraft system is a mechanically assisted FUE device which greatly speeds up the removal of follicular unit grafts from the donor area. One of the main drawbacks of follicular unit extraction is that it is a time consuming process which limits the amount of hairs that can be transplanted in one session. With the NeoGraft device, it is possible to perform larger mega-session style transplants in the same time as a normal manual FUE hair transplant.
With the NeoGraft device, the hair transplant surgeon uses an extraction device attached to the NeoGraft machine. A rotating sharp punch cuts into the tissue around the follicle and then air suction pulls the rest of the follicle into the machine where it is collected. When 50 follicular units have been extracted the follicles are removed from the machine and placed in saline to await being transplanted.
After the hair transplant doctor has cut the slits where the follicles will be transplanted, he uses a different device from the machine and suctions in one follicle into the device, which is then pushed into the transplant slit via air. Each follicle is individually transplanted this way.
Advantages of the NeoGraft System:
- The speed of extraction allows larger sessions to be done at one time, allowing follicular unit extraction mega-sessions.
- The follicles are touched very little if at all by human hands or forceps, preventing damage to the follicle.
Disadvantages of the NeoGraft System:
- Even more expensive than standard follicular unit extraction
- When the grafts are removed by suction, the tissue surrounding the base of the follicle is often removed, exposing the base of the follicle to air.
- The air suction and air moving through the machinery may cause follicles to dry and become desiccated, which is a major cause of follicle damage.
- When the follicles are reinserted via air pressure, there is no way to be sure the follicles are aligned properly and that the base of the follicle has not been folded.
SAFE System
 The SAFE system is a powered punch device. The powered unit rotates a blunt punch which removes the grafts by blunt dissection. As the SAFE device moves deeper into the tissue, the rotation of the punch slows to prevent damage to the follicle. The motorized punch increases the speed of the follicular removal and makes it easier on the hair transplant surgeon.
The SAFE system is a powered punch device. The powered unit rotates a blunt punch which removes the grafts by blunt dissection. As the SAFE device moves deeper into the tissue, the rotation of the punch slows to prevent damage to the follicle. The motorized punch increases the speed of the follicular removal and makes it easier on the hair transplant surgeon.
The rest of the procedure is performed the way a standard follicular unit extraction is. The grafts are removed by forceps and transplanted into the slits created by the hair transplant doctor.





